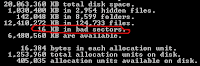
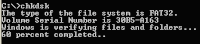DIR command is a DOS command that serves to display the files in a drive or folder is active.
This command is similar to the Copy command in the previous posts both on the run from the prompt drive.
This command is most often used for those who are accustomed to dealing with Command Prompt, do not continue to read, but for those who are unfamiliar please read carefully and try to practice the commands I give here.
Before executing the command DIR there are some things that must be understood as an active drive, the current folder.
Active Drive is the drive currently being accessed, as well as the folder is a folder that is used or diakes today.
How to do I know if the folder is active or being accessed at this time? Here's how to explain my logic, Suppose you from windows click Start - Run then type cmd and press enter when the cursor is (the sign minus karakater shaped guide flashing) is at C:\Document and Settings\user> then the current drive is now drive C and the current folder is the folder \Documents and Settings\ and sub folders on the \user>. and \user> usually can be changed to another name as a user in your computer.
So if you give DIR command (the command with a lowercase letter may be all), then all files and directories that display the files and folders in the sub folder \User>.
Various forms of DIR command, try the command (yellow) as the experimental materials and the early exercise to try in windows directory and then run the command below, do type the command: cd \windows and press Enter.
DIR and press command to display all files and all extensions
DIR *.* Enter, the command to display all files and all extensions
DIR? O *.* Enter, the command to display the file name from the left second letter is the letter O and the subsequent extensions free encyclopedia
DIR?? M *.* enter, the command to display the files from the left third letter is the letter m and the free extension
DIR *. c * Enter, the command to display the files and free the file name extension first letter is the letter C
DIR? O *. c * Enter, the command to display the file name both the letter of the file name is the letter O and the first letter of the extension is the letter c
DIR ?????.* Enter command to display the file names that only have 5 (five marks) or smaller letters, and free extensions
DIR *.?? Enter, the command to display files with the file name extensions freely while only 2 (two) letters only.
Maybe that's part of DIR command I can give, for later you can try with variations wildcards (special caracter * and?) On the DIR command to suit your needs.
Good luck with your practice with DOS commands
Read More
This command is similar to the Copy command in the previous posts both on the run from the prompt drive.
This command is most often used for those who are accustomed to dealing with Command Prompt, do not continue to read, but for those who are unfamiliar please read carefully and try to practice the commands I give here.
Before executing the command DIR there are some things that must be understood as an active drive, the current folder.
Active Drive is the drive currently being accessed, as well as the folder is a folder that is used or diakes today.
How to do I know if the folder is active or being accessed at this time? Here's how to explain my logic, Suppose you from windows click Start - Run then type cmd and press enter when the cursor is (the sign minus karakater shaped guide flashing) is at C:\Document and Settings\user> then the current drive is now drive C and the current folder is the folder \Documents and Settings\ and sub folders on the \user>. and \user> usually can be changed to another name as a user in your computer.
So if you give DIR command (the command with a lowercase letter may be all), then all files and directories that display the files and folders in the sub folder \User>.
Various forms of DIR command, try the command (yellow) as the experimental materials and the early exercise to try in windows directory and then run the command below, do type the command: cd \windows and press Enter.
DIR and press command to display all files and all extensions
DIR *.* Enter, the command to display all files and all extensions
DIR? O *.* Enter, the command to display the file name from the left second letter is the letter O and the subsequent extensions free encyclopedia
DIR?? M *.* enter, the command to display the files from the left third letter is the letter m and the free extension
DIR *. c * Enter, the command to display the files and free the file name extension first letter is the letter C
DIR? O *. c * Enter, the command to display the file name both the letter of the file name is the letter O and the first letter of the extension is the letter c
DIR ?????.* Enter command to display the file names that only have 5 (five marks) or smaller letters, and free extensions
DIR *.?? Enter, the command to display files with the file name extensions freely while only 2 (two) letters only.
Maybe that's part of DIR command I can give, for later you can try with variations wildcards (special caracter * and?) On the DIR command to suit your needs.
Good luck with your practice with DOS commands